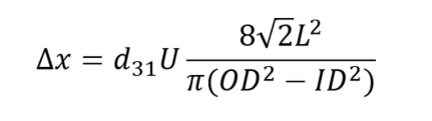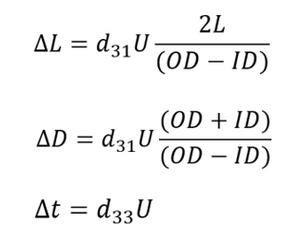- Lowest tolerances (0.05 mm)
- Large variety of outside diameters (0.5 mm to 150 mm)
- Metallizations with thin and thick layer technology, wrap-around contact is possible
- Segmented electrodes for lateral displacements
- Industrial-grade assembly with wire, stranded wire or flex board contacting
- Protective coatings
- Glas fiber bonding
Applying a voltage causes changes in the diameter, axial length, and wall thickness of piezoceramic tubes. By using segmented electrodes, precise lateral displacements can be achieved through controlled bending. These highly accurate and ultra-fast movements have a wide range of applications — from microdosing and inkjet printing, to the precise positioning of small objects, the manipulation of glass fibers, and the generation of ultrasound. Tailored, application-specific characteristics can be achieved through targeted refinement of the piezoelectric components.
Specifications
Whether a customized design or a standard product – PI Ceramic offers comprehensive support ranging from the selection of the optimal material to the development of solution-oriented applications. The dimensions of the piezo tubes can be flexibly defined within specified tolerance ranges. Feasibility can only be assessed once the desired specifications or application requirements are provided.
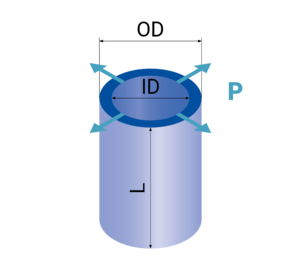
| Outer diameter OD [mm] | 0.5 - 150 |
| Inner diameter ID [mm] | 0.3 - 140 |
| Length L [mm] | Max. 70 |
| Electrodes | Outside: thick film (Ag), thin film (Ag, Au, CuNi, Cu, NiV, Cr), electroless nickel (from ID > 1 mm) Inside: thick film (Ag), electroless nickel (from ID > 1 mm) |
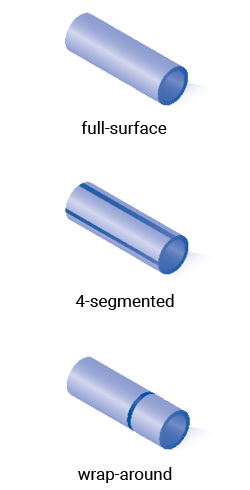
| Electrode designs | In addition to multi-segmented tubes, other designs are possible, such as full-surface, 4‑segmented or wrap‑around. See right column. |
| Termination | A variety of contacting methods are available, including soldering or bonding wires, strands, and flex boards. With the help of special adapters, even small four-segmented tubes can be easily contacted under a microscope — without compromising functionality. The datasheet is available >> here. |
| Polarization direction | Depending on the contacting and attachment of the electrodes, different bending occur in the axial, radial and lateral directions. For more information see >> Operating Modes. |
| Material | We offer various ferroelectric soft and hard PTZ materials. |
| Added capabilitites | In addition to refinement via assembly and interconnection techniques, tailored, ready-to-use piezo components can be developed, including
|
| Applications | Piezoceramic tubes are well-suited for a variety of sensor and actuator applications. Examples of potential uses can be found >> here. |
Operation Modes
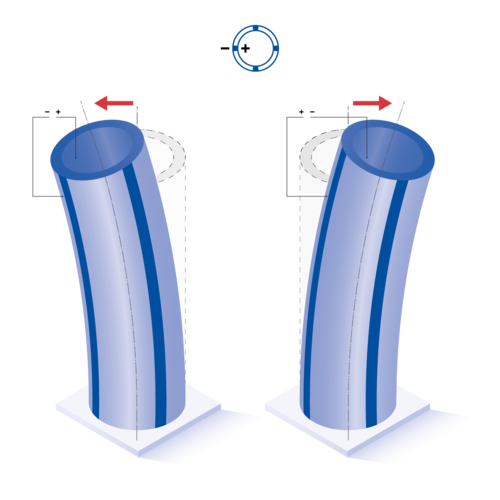
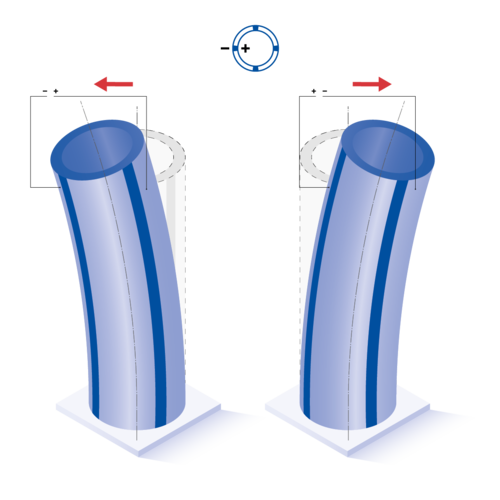
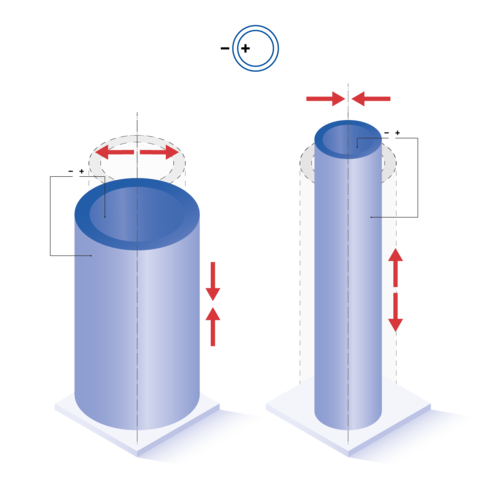
When piezo tubes are used as actuators, applying an electrical voltage causes mechanical deflection. This deflection can take the form of static deformation when a DC voltage is applied, or oscillatory motion — such as in the ultrasonic range — when driven by an AC voltage. Depending on the design of the piezo component, the motion can occur either axially or laterally. The amplitude of the deflection is influenced by both the dimensions of the piezo tube and the magnitude of the applied voltage.
For example, for tubes with positive polarization direction on the inside and negative polarization direction on the outside, the deflection directions are as follows:
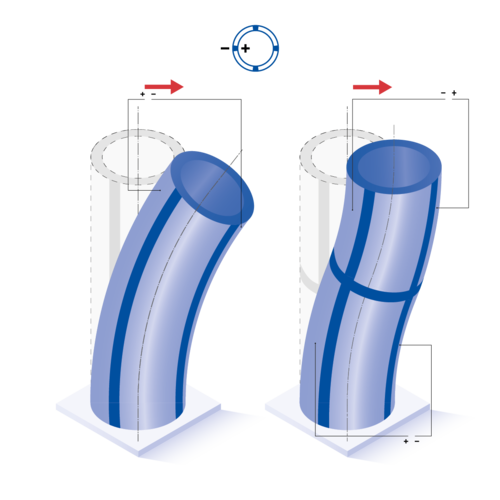
4-segmented tube: Lateral deflection occurs when the inner electrode and one outer segment are activated, as well as when two opposing outer segments are driven simultaneously.
Red arrows indicate the direction of deformation.
All formulas shown are valid for idealized geometries (ID, OD >> t). Tubes with negative polarization direction as well as internal ground (GND) show opposite displacement directions.
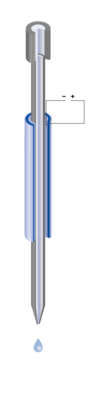
Glass Capillary Bonding
Piezo tubes can be used in the field of medical and industrial microdosing. Special contacting and control of the tubes generate targeted pressure pulses. These result in the precise delivery of fluid from a capillary in the picoliter range. In addition to customized manufacturing of piezo tubes, PI Ceramic has the expertise to bond them with ultrafine glass capillaries from our customers.
- Intravascular lithotripsy
- Atrial fibrillation intravascular catheters
- Intravascular ultrasound imaging
- Microarray spotting
- Ultrasonic needle tip tracking
- Scanning fiber endoscopy
- Atomic force microscopy
- Precision dosing and inkjet printing
- Underwater communication
- Micromanipulation
- Scanning tunnel microscopy
Downloads
Material Data
Datasheet Tubes with Connector
User Manual A000T0047
Handling and Electrical Contacting of Piezo Components